SEBI Made Simple: Protecting Your Money with Ease!
Investing in the financial markets can be daunting, especially for those new to the game. With so many complexities and risks involved, it’s essential to have a regulatory body that safeguards investors’ interests. This is where the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) steps in. Established in 1988, SEBI plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning and integrity of the Indian securities market.
What is SEBI?
SEBI, which stands for Securities and Exchange Board of India, is the regulatory authority responsible for overseeing the securities markets in India. Established in 1988 under the SEBI Act, 1992, SEBI works under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance. Its primary role is to protect the interests of investors and ensure the smooth functioning of the securities market by enforcing regulations, promoting transparency and maintaining market integrity.
SEBI regulates various entities and activities in the securities market including stock exchanges, brokers, merchant bankers and mutual funds. It also plays an important role in promoting investor education and awareness to empower investors to take informed investment decisions. Overall, SEBI’s presence is important to enhance investor confidence, attract investments and facilitate economic growth in India.
History Of SEBI
SEBI, the Securities and Exchange Board of India, was established in 1988 as a non-statutory body to regulate the securities market. In 1992, the SEBI Act was enacted, granting statutory powers to SEBI. Over the years, SEBI underwent significant regulatory reforms, expanding its authority to cover various segments of the securities market. It introduced market reforms, prioritized investor protection initiatives, and collaborated with international regulatory bodies. Today, SEBI stands as a robust regulatory authority, playing a vital role in maintaining the integrity and stability of India’s securities market.
Importance of SEBI in financial markets
- Investor Protection: SEBI’s foremost objective is to safeguard the interests of investors. By implementing stringent regulations and oversight mechanisms, SEBI aims to protect investors from fraudulent activities, market manipulations, and unfair practices. This instills confidence among investors and encourages participation in the securities market.
- Market Transparency and Fairness: SEBI promotes transparency and fairness in the market by enforcing disclosure requirements and regulating market participants. Companies are mandated to disclose accurate and timely information, ensuring that investors have access to essential data to make informed investment decisions. Additionally, SEBI regulates trading practices to maintain a level playing field for all market participants.
- Regulatory Oversight: As the regulatory authority for the securities market, SEBI formulates rules and regulations to govern various aspects of market activities. It regulates stock exchanges, intermediaries such as brokers and merchant bankers, and securities offerings to ensure compliance with laws and regulations. This regulatory oversight helps maintain market integrity and protects investors from market abuses.
- Market Development: SEBI plays a crucial role in fostering the development and growth of the securities market. It introduces new financial instruments, promotes innovations, and enhances market infrastructure to meet the evolving needs of investors and issuers. By facilitating a conducive environment for market development, SEBI contributes to the overall expansion and sophistication of the financial markets in India.
- Foreign Investments: SEBI’s regulatory framework and oversight mechanisms also play a significant role in attracting foreign investments into the Indian securities market. By ensuring transparency, fairness, and investor protection, SEBI enhances the credibility of the Indian market, making it an attractive destination for foreign investors seeking investment opportunities.
ALSO READ: RBI Policy: Das Says Rate Stance Clear, but Transmission Incomplete
Functions of SEBI
- Regulatory Functions: SEBI formulates and enforces regulations to govern various entities and activities within the securities market. This includes:
- Regulating stock exchanges: SEBI oversees the operations of stock exchanges to ensure fair and transparent trading practices. It monitors trading activities, enforces listing requirements, and takes action against any misconduct or violations.
- Regulating intermediaries: SEBI regulates intermediaries such as brokers, merchant bankers, and portfolio managers. It sets guidelines for their conduct, registration, and compliance with regulations to protect investors’ interests and maintain market integrity.
- Enforcing securities laws: SEBI enforces securities laws and regulations to prevent market abuse, insider trading, and fraudulent activities. It investigates complaints, conducts inspections, and imposes penalties on entities found violating the law.
- Developmental Functions: SEBI works towards the development and expansion of the securities market by introducing new initiatives and promoting innovations. This includes:
- Introducing new financial instruments: SEBI introduces new financial products and instruments to diversify investment opportunities and meet the evolving needs of investors and issuers.
- Promoting investor education: SEBI conducts investor awareness programs and initiatives to educate investors about market risks, investment strategies, and regulatory compliance. By enhancing financial literacy, SEBI empowers investors to make informed decisions.
- Enhancing market infrastructure: SEBI focuses on enhancing market infrastructure, such as trading platforms and settlement systems, to improve market efficiency, transparency, and accessibility.
- Protective Functions: SEBI is committed to protecting investors’ interests and ensuring market integrity. This includes:
- Safeguarding investors: SEBI implements measures to protect investors from fraudulent practices, market manipulations, and unfair trading practices. It imposes disclosure requirements, prohibits insider trading, and provides mechanisms for redressal of investor grievances.
- Monitoring market activities: SEBI closely monitors market activities, including trading volumes, price movements, and investor behaviors, to detect any irregularities or misconduct. It takes proactive measures to maintain market stability and investor confidence.
- Promoting fair practices: SEBI promotes fair and transparent practices by market participants through regulations, guidelines, and enforcement actions. It fosters a culture of compliance and integrity to ensure a level playing field for all market participants.
Organisational Structures Of SEBI
- Board of Directors: The SEBI Board consists of a chairman, nominated members from the Government of India, and professionals with experience in securities markets. The board sets policies, oversees operations, and ensures regulatory compliance.
- Committees: SEBI has various committees, such as the Audit Committee, Regulatory Policy Committee, and Market Advisory Committee, composed of SEBI officials and external experts. These committees assist in policy formulation, regulatory oversight, and decision-making.
- Departments: SEBI has multiple departments responsible for specific functions, including regulation and supervision of market intermediaries, surveillance of market activities, enforcement of regulations, investor education and protection, and policy formulation.
- Regional Offices: SEBI operates regional offices across major cities in India to facilitate regulatory compliance, surveillance, and investor grievance redressal at the grassroots level.
- Market Intermediaries: SEBI regulates various market intermediaries, including stock exchanges, brokers, merchant bankers, and mutual funds. These intermediaries are required to comply with SEBI regulations and guidelines.
- Investor Protection Funds: SEBI manages investor protection funds established to compensate investors in case of default by market intermediaries or fraudulent activities.
Investor Protection Measures
- Disclosure Requirements: SEBI mandates companies to disclose accurate and timely information to investors. This includes financial statements, corporate actions, and any material information that may impact the company’s securities. By providing transparency, investors can make informed decisions.
- Prohibition of Insider Trading: SEBI prohibits insiders from trading based on unpublished price-sensitive information. This regulation prevents unfair advantages and protects the integrity of the market. Insider trading is strictly monitored and enforced to maintain market fairness.
- Redressal of Investor Grievances: SEBI provides a platform for investors to file complaints against market participants for any misconduct or fraud. It ensures prompt redressal of grievances through mechanisms such as investor helplines, online complaint filing systems, and investor protection funds.
- Education and Awareness Programs: SEBI conducts investor education programs and initiatives to enhance financial literacy among investors. These programs aim to educate investors about market risks, investment strategies, and regulatory compliance. By empowering investors with knowledge, SEBI helps them make informed decisions.
- Risk Mitigation Measures: SEBI implements risk mitigation measures to protect investors from market volatility and systemic risks. This includes setting trading limits, circuit breakers, and margin requirements to ensure market stability and prevent excessive speculation.
- Regulation of Intermediaries: SEBI regulates intermediaries such as brokers, mutual funds, and investment advisors to ensure their conduct aligns with investor interests. It sets guidelines for their registration, conduct, and compliance with regulations to maintain market integrity.
- Monitoring and Surveillance: SEBI conducts monitoring and surveillance of market activities to detect any irregularities or manipulative practices. Through sophisticated surveillance systems and data analytics, SEBI identifies suspicious activities and takes prompt enforcement actions.
- Enforcement of Regulations: SEBI enforces strict compliance with regulations through penalties, sanctions, and enforcement actions against entities violating securities laws. This includes fines, suspension or cancellation of licenses, and legal proceedings to deter misconduct and protect investors.
Powers Of SEBI
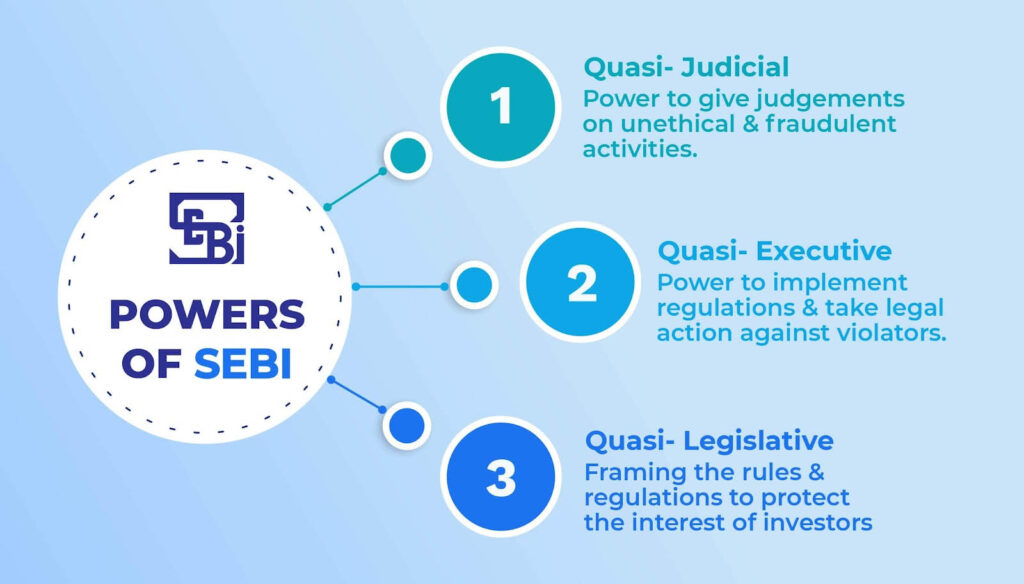
- Regulatory Authority: SEBI has the authority to regulate various entities and activities in the securities market, including stock exchanges, brokers, merchant bankers, and listed companies. It formulates rules, regulations, and guidelines to govern their conduct and operations.
- Rulemaking: SEBI can make regulations and issue guidelines to govern different aspects of the securities market, such as listing requirements, disclosure norms, trading practices, and investor protection measures. These regulations are enforced to maintain market integrity and protect investors’ interests.
- Enforcement: SEBI has enforcement powers to ensure compliance with securities laws and regulations. It can conduct investigations, inspections, and audits of market participants to detect violations and take enforcement actions, including imposing fines, penalties, and sanctions for non-compliance.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: SEBI monitors market activities, including trading volumes, price movements, and investor behaviors, to detect any irregularities, market manipulations, or insider trading activities. It employs sophisticated surveillance systems and data analytics to maintain market integrity and stability.
- Adjudication: SEBI has the authority to adjudicate disputes, complaints, and regulatory violations through its quasi-judicial process. It can conduct hearings, pass orders, and impose sanctions on entities found guilty of securities law violations.
- Investor Protection: SEBI is empowered to implement measures to protect investors’ interests, including disclosure requirements, prohibition of insider trading, redressal of investor grievances, and compensation through investor protection funds in case of defaults or frauds by market intermediaries.
- Market Development: SEBI promotes market development by introducing new products, enhancing market infrastructure, and fostering innovations in the securities market. It facilitates capital formation, liquidity, and efficiency in the market to attract investments and support economic growth.
How SEBI Protects Your Money
- Ensuring Fair Practices by Market Participants: SEBI regulates market intermediaries, including brokers, merchant bankers, and stock exchanges, to ensure fair and transparent practices. By imposing strict guidelines and monitoring their conduct, SEBI prevents malpractices such as fraudulent trading, misappropriation of funds, and market manipulation, thus safeguarding investors’ money.
- Monitoring and Regulating Securities Markets: SEBI closely monitors the functioning of securities markets, including equity, derivatives, and commodities markets. Through surveillance systems and real-time monitoring, SEBI detects irregularities, abnormal price movements, and manipulative activities. By taking timely action, such as imposing trading restrictions or suspending trading in certain securities, SEBI protects investors from potential losses due to market volatility or misconduct.
- Promoting Investor Education and Awareness: SEBI conducts investor education programs and initiatives to enhance investors’ understanding of market risks, investment products, and regulatory compliance. By empowering investors with knowledge and information, SEBI enables them to make informed investment decisions and avoid potential pitfalls that could lead to financial losses.
- Regulating Investment Products and Schemes: SEBI regulates various investment products and schemes, including mutual funds, alternative investment funds (AIFs), and collective investment schemes (CIS). By setting stringent regulations, disclosure requirements, and investment restrictions, SEBI ensures the integrity and transparency of these products, protecting investors’ interests and funds.
- Enforcing Investor Protection Measures: SEBI enforces investor protection measures such as disclosure requirements, prohibition of insider trading, and redressal of investor grievances. Companies are required to disclose relevant information to investors, insiders are prohibited from trading based on unpublished price-sensitive information, and investors have access to mechanisms for filing complaints and seeking redressal of grievances. Through these measures, SEBI aims to safeguard investors’ money and ensure their rights are protected.
Key Regulations by SEBI
- Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements: SEBI mandates listed companies to adhere to stringent listing obligations and disclosure requirements. This includes periodic financial reporting, disclosure of material information, and adherence to corporate governance norms. By ensuring transparency and accountability, this regulation protects investors’ interests and fosters market integrity.
- Takeover Regulations: SEBI regulates corporate takeovers to ensure fair treatment of shareholders and prevent any coercive or unfair practices by acquirers. The takeover code, formulated by SEBI, sets guidelines and thresholds for open offers and mandates disclosures to protect minority shareholders’ interests. This regulation promotes transparency and safeguards investors’ rights during takeover transactions.
- Mutual Fund Regulations: SEBI regulates the mutual fund industry to protect investors’ interests and promote transparency, accountability, and professionalism among fund managers and asset management companies. The regulations cover various aspects of mutual fund operations, including fund management, disclosures, investor protection measures, and distribution practices. By setting standards and guidelines, SEBI ensures the integrity and stability of the mutual fund industry, thereby safeguarding investors’ investments.
- Insider Trading Regulations: SEBI prohibits insider trading, whereby insiders trade securities based on unpublished price-sensitive information. SEBI’s insider trading regulations aim to prevent unfair advantages and market abuse by insiders and ensure a level playing field for all investors. The regulations impose strict penalties and sanctions for violations, thereby deterring insider trading activities and protecting investors’ interests.
- Corporate Governance Norms: SEBI has introduced corporate governance norms for listed companies to promote transparency, accountability, and integrity in corporate practices. These norms cover board composition, disclosure requirements, audit practices, and shareholder rights. By fostering good corporate governance practices, SEBI enhances investor confidence and protects shareholders’ interests.
- Margin Trading Regulations: SEBI regulates margin trading to prevent excessive speculation and market manipulation. Margin trading involves borrowing funds to invest in securities, and SEBI’s regulations set limits on margin exposure, collateral requirements, and risk management practices. By ensuring prudent margin trading practices, SEBI protects investors from potential losses and maintains market stability.
- Investor Protection Regulations: SEBI has implemented various investor protection regulations, including disclosure requirements, grievance redressal mechanisms, and stringent enforcement measures. These regulations aim to safeguard investors’ interests, promote transparency, and ensure fair treatment of investors by market participants. By providing avenues for investor protection and enforcing compliance, SEBI enhances investor confidence and trust in the securities market.
SEBI Made Simple: Tips for Investors
For investors looking to navigate the securities market with ease, here are some tips:
- Understand your investment options: Research and understand the various investment avenues available and choose ones that align with your financial goals and risk appetite.
- Stay updated with market regulations: Keep yourself informed about the latest market developments and regulatory changes to make informed investment decisions.
- Seek professional advice if needed: If you’re unsure about where to invest or how to manage your portfolio, consider seeking advice from a qualified financial advisor to help you make sound investment choices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SEBI plays a vital role in protecting investors’ interests and maintaining the integrity of the securities market in India. By enforcing regulations, promoting transparency, and fostering investor education, SEBI ensures a fair and efficient market environment for all participants.
FAQs
- What is SEBI’s role in the Indian securities market? SEBI regulates the securities market in India to protect investors’ interests, promote transparency, and maintain market integrity.
- How does SEBI protect investors’ funds? SEBI implements various measures such as disclosure requirements, prohibition of insider trading, and redressal of investor grievances to safeguard investors’ funds.
- What are some key regulations introduced by SEBI? SEBI has introduced regulations regarding listing obligations, takeover, and mutual funds to govern different aspects of the securities market.
- How can investors stay updated with market regulations? Investors can stay updated with market regulations by following SEBI’s announcements, attending investor awareness programs, and seeking advice from financial experts.
- Why is it essential for investors to understand market regulations? Understanding market regulations helps investors make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and protect their investments from fraudulent activities.




